What Is Vascular Dementia?
Vascular dementia is the second most common disease on the list. It is directly behind Alzheimer’s disease. This form of dementia is involved in 10 to 20% of cases.
Like all types of dementia, the disease process is characterized by cognitive impairment. This refers to the loss or deterioration of some mental faculties such as:
- memory
- reason
- behaviour
Vascular dementia is caused by damage caused by cerebrovascular disease. What happens is that certain parts of the brain don’t get enough blood supply and eventually get damaged. In this article, we explain why it occurs, as well as its symptoms and treatment.
What is Vascular Dementia?
To diagnose vascular dementia, some basic requirements must be met. First of all, there are criteria for dementia. As we mentioned above, the criteria are based on the deterioration of mental abilities. To measure this deterioration, doctors use various tests and questionnaires.
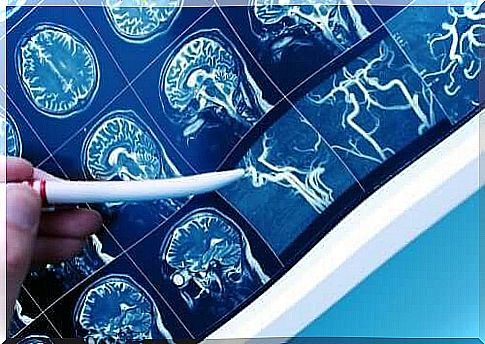
On the other hand , there must be evidence of cerebrovascular disease. This can be seen with a history of vascular problems or certain signs during the physical examination. Medical professionals also rely on imaging such as CT or MRI scans to determine the possible brain injury.
A stroke can cause vascular dementia, but it won’t always happen. Vascular dementia can also be caused by other conditions that affect the blood vessels. Any condition that reduces cerebral blood flow, such as atherosclerosis, can cause it.
There are several risk factors that increase the risk of vascular dementia. Thus, controlling these factors can reduce its incidence. This involves various factors such as:
- suffer from diabetes
- hypertension
- high cholesterol
- to smoke
Symptoms

The symptoms of vascular dementia vary depending on the part of the brain that has reduced blood flow. In general, the symptoms are similar to those of other types of dementia.
First of all , the patient may feel disoriented and have difficulty concentrating. Their ability to organize their thoughts also diminishes. One of the most alarming symptoms is memory loss. Other common symptoms include:
- Unstable gait.
- Inability to control the release of urine.
- Difficulty performing tasks that used to be easy for the patient.
- Problems with language.
- Changes in mood or personality.
- Loss of social skills.
- Depression.
- Sleep disorders.
- Hallucinations or delusions.
The symptoms can be more obvious and very sudden when they manifest after a stroke. In other cases , the symptoms progressively worsen. This usually allows a differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, which usually develops gradually.
However, this condition can also develop subtly and gradually. As the disease progresses, the symptoms become more apparent and severe. Patients with vascular dementia can eventually no longer care for themselves.
How to Prevent Vascular Dementia
Protecting the health of the blood vessels is essential. As we mentioned above, maintaining normal blood pressure is one of the most important steps.
- You also need to control or prevent diabetes.
- It is advisable to follow a good diet and get plenty of exercise.
- On the other hand, it is very important to stop smoking because tobacco damages the blood vessels.
- In the same way, you need to maintain good cholesterol levels. That is, because it can help reduce the risk of stroke. That is why the diet you follow is so important.
You should pay attention to all these preventive measures. The reason is that there is no effective treatment for vascular dementia. Treatment usually focuses on managing the risk factors.
How is vascular dementia diagnosed?
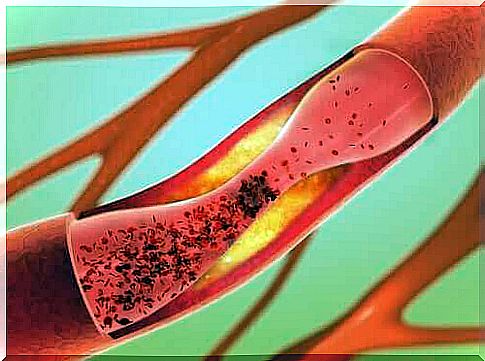
This condition is diagnosed by the likelihood that the patient’s symptoms are caused by a vascular problem. This probability increases depending on:
- the patient’s stroke history
- whether there are already other heart or blood vessel disorders.
Blood tests are also performed to make the diagnosis. The medical professionals focus on cholesterol and blood sugar levels and are also on the lookout for anemia or other conditions. In addition, imaging tests and ultrasounds of the carotid arteries are performed to determine the condition.
Neuropsychological tests also help to distinguish between the different types of dementia. Medical professionals evaluate the patient’s ability to speak, write, and work with numbers, among other things.
Patients suffering from vascular dementia often find it more difficult to analyze a problem. However, they have less difficulty learning and remembering information than people with Alzheimer’s.
Conclusion
It is very important to have a healthy lifestyle to prevent vascular dementia. Watching what you eat and exercising are two fundamental pillars of prevention. However, if you notice any warning signs, don’t hesitate to see your doctor as soon as possible.