The Causes And Diagnosis Of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of death. In this article, we discuss the causes and diagnosis of lung cancer.
Unfortunately, it is a difficult disease to detect in the early stages. This makes it difficult to start an effective treatment in time. Because the diagnosis often comes later, treatments for advanced stages of lung cancer are often not optimistic.
In most cases, cells can detect and repair damaged DNA. If a cell is severely damaged and unable to repair itself, it triggers programmed cell death or apoptosis.
The exact cause of lung cancer is still under investigation. However, it has been proven that certain risk factors can make body cells cancerous. These risk factors are determined by, among other things, heredity and exposure to, for example, radiation. However, the most obvious factor is tobacco use.
Tobacco use

With the introduction of the first cigarette rollers in 1876, tobacco became accessible to many people. At that time, this type of cancer was not common. As time went on, smoking became more and more popular. The number of lung cancer cases also increased.
Currently, about 85% of all lung cancer cases are related to tobacco use. Radon gas, pollution, toxins and other factors contribute to the remaining 15%.
Both cigarettes and cigarette smoke contain more than 70 cancer-causing chemicals. Some of them are the following:
- Arsenic (an insecticide)
- Benzene (a gasoline additive)
- Lead (a highly toxic metal)
- Cadmium (also found in batteries and accumulators)
- Isoprene (used to make synthetic rubber)
The importance of the cilia
Cigarette smoke can reduce or paralyze the functioning of the cilia, the cilia in the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract.
The cilia are responsible for eliminating toxins, carcinogens, viruses and bacteria. When cigarette smoke damages or destroys the cilia, all the harmful elements can build up in the lungs. This causes a variety of problems. These can range from infections to cancer.
Risk Factors
- genetics. Unfortunately, there are patients who develop lung cancer without any related medical history.
- Drinking water containing a high concentration of arsenic. This can increase the chance of developing the disease. However, it is not clear how this process works.
- Tobacco use. Although we still don’t know what causes adenocarcinoma in the lungs, it is more common in smokers than in non-smokers. Among the most common risk factors are secondhand smoke, radon gas, air pollution and occupational exposure.
Secondhand smoke
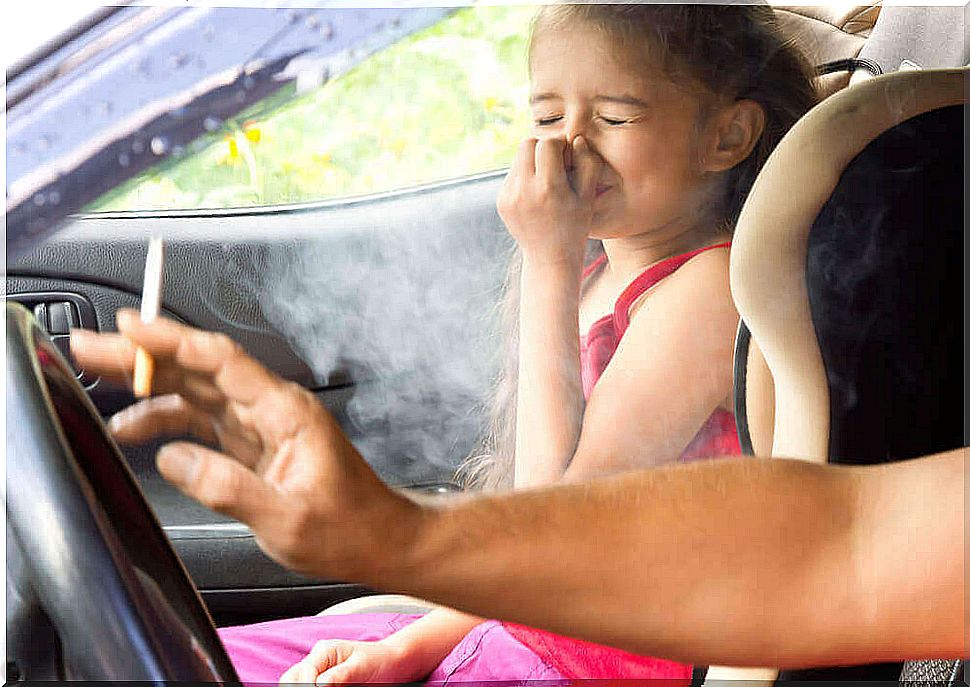

People who smoke not only increase their own risk of developing lung cancer, but that of others as well. A non-smoker who lives with a smoker has a 20% to 30% higher chance of developing this disease. This is due to exposure to smoke concentrations in his or her environment.
Radon
Radon gas is a radioactive gas. If it breaks down into other dust particles and is inhaled, it can settle on lung tissue. The radiation emitted can subsequently damage the tissue.
Smokers exposed to this gas are at a higher risk of developing the disease than non-smokers. Radon gas is a natural gas, but it can seep into homes and build up in basements and crawl spaces.
air pollution
Air pollution also contributes to the development of lung cancer. The pollutants carried through the air, such as diesel smoke, can cause some people to develop this disease. It is estimated that about 5% of lung cancer cases are caused by air pollutants.
Occupational exposure
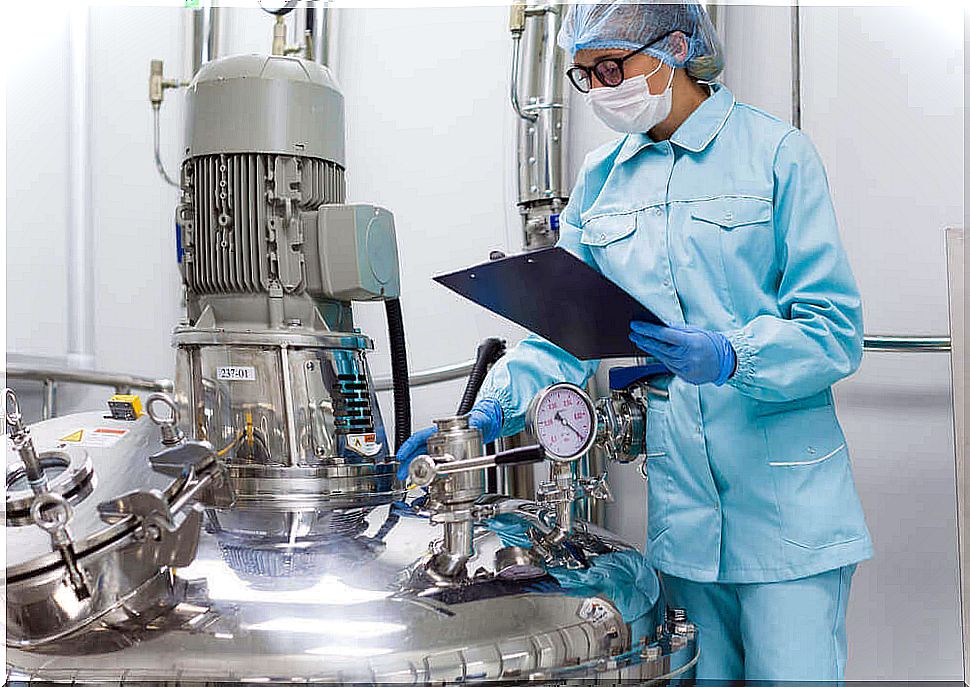

As mentioned, smoking is the biggest risk factor for the development of this type of cancer. However, exposure to certain chemical components and products is another risk factor.
Chemicals such as asbestos, arsenic and benzene increase the risk of developing lung cancer.
Exposure to asbestos can even cause lung cancer (mesothelioma) many years after the first exposure. These people are at risk of living with this cancer for decades. Sometimes 30 to 40 years.
Symptoms
When a person with lung cancer develops symptoms, the most common symptoms they experience are:
- Fatigue
- Chestpain
- weight loss
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Chronic cough, coughing up blood
Types of Lung Cancer
- Small cell lung cancer. This type accounts for about 15% of total cases. This type of lung cancer usually spreads quickly.
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. This is the most common type. It represents about 80% of all lung cancer cases and is not as aggressive. In other words, it spreads to other tissues and organs at a slower rate.
Different types of cancer can have metastases in the lungs. However, these are not considered lung cancers.
Diagnosis
Unfortunately, the early stages often show no visible symptoms that indicate that something serious is wrong with us. In many cases, the symptoms are general. As a result, we often do not suspect cancer.
About 25% of people who don’t show symptoms are diagnosed with lung cancer through a chest X-ray or during a routine test.
If the routine tests indicate lung cancer, the doctor should continue testing to confirm the diagnosis. Among other things, a medical specialist can perform pathological examinations to classify and determine the stage of the lung cancer.
Lung Cancer Prevention

The most recommended (and obvious) method of prevention is to avoid tobacco use. Or at the very least, you should significantly reduce the habit.
Smokers who quit smoking can reduce their risk of lung cancer. After ten years, they are at the same risk as someone who does not smoke.
In addition, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, avoid excesses and take precautions with chemicals and toxic substances in general.